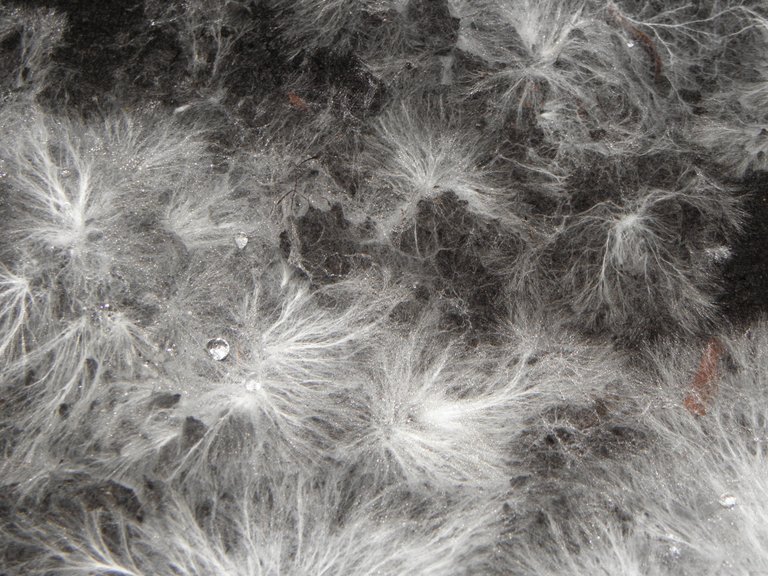
You probably shouldn't eat moldy foods because eating lots of molds at once is dangerous to the health but in contrast, eating little amounts of mold at a time might not do much to ones health unless in the case of being allergic but eating this little moldy food repeatedly for a long period of time can lead to serious health problems including risk of cancers kidney and liver diseases.
The majority opinion about food safety and health expert is that if it is moldy, you shouldn't eat it. This is because what you see in the surface is little compared to the hyphae the mold in the food. Not all molds are dangerous by existence, some molds are beneficial like those found in some cheese. Before we continue to bore ourselves with the mold talk, what are molds?
In simple words, molds are fungi and fungi are similar to plants but do not photosynthesize which means they do not produce their own food rather they feed on organic matters, that is why you can find them on breads, and other foods. Molds are fungi, but they aren't mushrooms but are similar to mushrooms in a lot of molecular ways. Mushrooms are like trees with their root equivalents underground and their body and fruits which includes its stem, cap, and gills to reproduce. We can say that mold is to mushrooms as green algae is to plant.
Molds are threads of fungal cells known as Mycelium with its single thread being the hyphae. Which molds get us sick, we can have some suspects such as Blue Green molds like Penicillia, or Cladosporium, or the black and gray mold which includes Rhizopus, Mucorales, and Aspergillus. You can begin to wonder if molds do not die when they are not on organic matters, and the answer is that their spores are resilient which means they can survive in the environment while being dormant for a very long time until they come in contact with an organic matter like the bread you are bringing to the table.
How dangerous are the molds we find on our food? Asides from the enzymes that molds produce in other to feed, they also produce metabolites such as the one associated with the wet basement smell, and secondary metabolites which are not necessary for their growth and reproduction and these metabolites can be toxic to us in what we refer to as mycotoxins. Why these secondary metabolites are produced, and when they are produced, but they cause acute toxicity.
Chronic exposure to mycotoxins overtime has been associated with numerous health conditions including immune deficiency, and even cancer according to the World Health Organization. Acute symptoms of mycotoxins in animals includes liver, spleen, and kidney damage.
While not all molds are dangerous, it's essential to exercise caution and adhere to the general advice: if a food item is moldy, it's safer to avoid consuming it. Regular awareness of food safety practices can contribute to overall well-being and mitigate potential health risks associated with mold exposure.
Sources
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2214799319300608
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/10.1080/15569543.2020.1795685
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mycotoxins
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27030861/
https://www.micropia.nl/en/discover/microbiology/mycelium/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC164220/
https://www.fda.gov/food/natural-toxins-food/mycotoxins