"Neuroscience, or neurology" a very familiar word or part of science that we cannot overlook when discussing the science of humans or living thing in general. You ask why? the answer is simple. It is the science that studies the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. That said, to Neuroscience encompasses different areas and I will be explaining them in this post.
When we talk about neuroscience, we cannot but mention the brain structure. The brain is divided into two hemisphere which are the right and the left hemisphere and the brain stem. The brain stem is made up of the medulla oblongata, the pons, the midbrain, and the interbrain which is the largest part of the brain stem. You know, the cerebellum is sometimes included in the brain stem since it is located behind the medulla oblongata.
The medulla oblongata have center for reflexes for blinking, coughing, vomiting, sneezing, respiration, digestion, and blood circulation. The cerebellum is responsible for receiving information from motor centers of the cerebellar cortex, muscles, and tendons, and this is why the cerebellum is able to control posture, muscle tone, and balance. Talking about muscle tone also, the white matter of the midbrain contains the nuclei which is responsible for regulating muscle tone.
The thalamus and the hypothalamus are located at the diencephalon (intermediate brain) with the Thalamus responsible for regulating sleep and wakefulness, formation of emotion, and complex movement. The hypothalamus on the other hand regulate metabolism, ensuring there is homeostasis in the internal environment, and regulates the autonomic nervous system. The Thalamus has an endocrine gland above it known as the Epiphysis, and the Hypothalamus is connected to the pituitary gland. The division of the Cerebrum hemisphere is connected by the Corpus Callosum, These hermispheres are known as the cerebral cortex which is formed by gray matter.
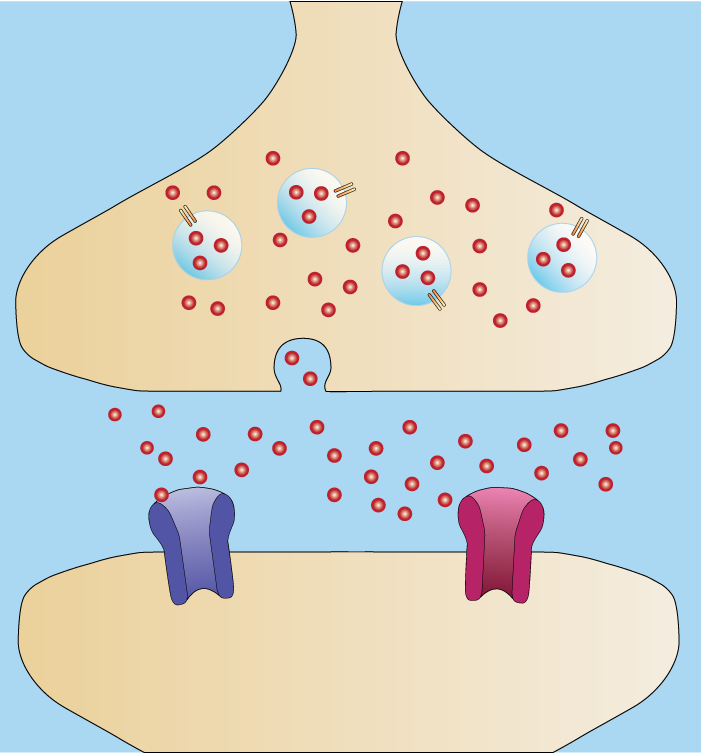
After discussing the brain structure, we cannot mention neuroscience without mentioning neurotransmitters. These are chemical substances that transmit signals between nerve cells (neurons) and the the body. They transmit the nerve signals when secreted from the nerve ending of one neuron (the presynaptic neuron), and act on the receptor of the next neuron (postsynaptic neuron) or the cells to be targeted.
Acetylcholine is a type of neurotransmitter and it is responsible for muscle stimulation, activation of motor neurons, as well as involved in areas of the brain related to learning, memory, arousal, and it is responsible for changing ones state from vigilance to sleep state. Another neurotransmitter is dopamine which we know as the pleasure, or feel good neurotransmitter. Dopamine plays important role in decision making, learning, and memory regulation.
Also, we have noradrenaline which serves as a hormone and a neurotransmitter. It is refered to as the stress hormone, and as a neurotransmitter, it activates the sympathetic nervous system and also regulates the physical and mental arousal state. We cannot but mention Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which is responsible for inhibitory functions including preventing over-excitement, inducing anxiety and fear. Other neurotransmitters in the body are Glutamate, Serotonin, and so on.
While we mention neurotransmitter, we would mention synapses which are the gaps between two cells. when we mention that, we have two types of synaptic cells which are the presynaptic cells and the postsynaptic cells, and in these cells, two types of reactions can occur and they are the chemical reaction and the electrical reactions.
In delving into neuroscience, we embark on a journey of discovery, unraveling the complexities of the human brain and its profound implications for our understanding of health, behavior, and consciousness. Through ongoing research and exploration, we continue to unlock the secrets of the nervous system, illuminating the pathways to deeper insights into the essence of human existence.
https://www.kcl.ac.uk/neuroscience/about/what-is-neuroscience
https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/neuro/conditioninfo
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549789/
https://mayfieldclinic.com/pe-anatbrain.htm
https://med.libretexts.org/Bookshelves
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9136724/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542184/
https://www.aans.org/en/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Anatomy-of-the-Brain
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539894/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9180936/